As a medical professional, I often prescribe Wellbutrin, also known by its generic name bupropion. This medication is a bit different from the standard antidepressants you hear about. Unlike the more common SSRIs (like Prozac or Zoloft) that mainly focus on serotonin, Wellbutrin primarily affects the brain chemicals dopamine and norepinephrine.
This unique mechanism of action gives Wellbutrin distinct advantages, particularly in terms of side effects, many patients find it doesn’t cause the sexual side effects or weight gain often associated with other medications. However, it also has its own specific risks and side effects that you need to be aware of. Let’s talk clearly and simply about what this medication does and how to use it safely.
How Wellbutrin Works Differently
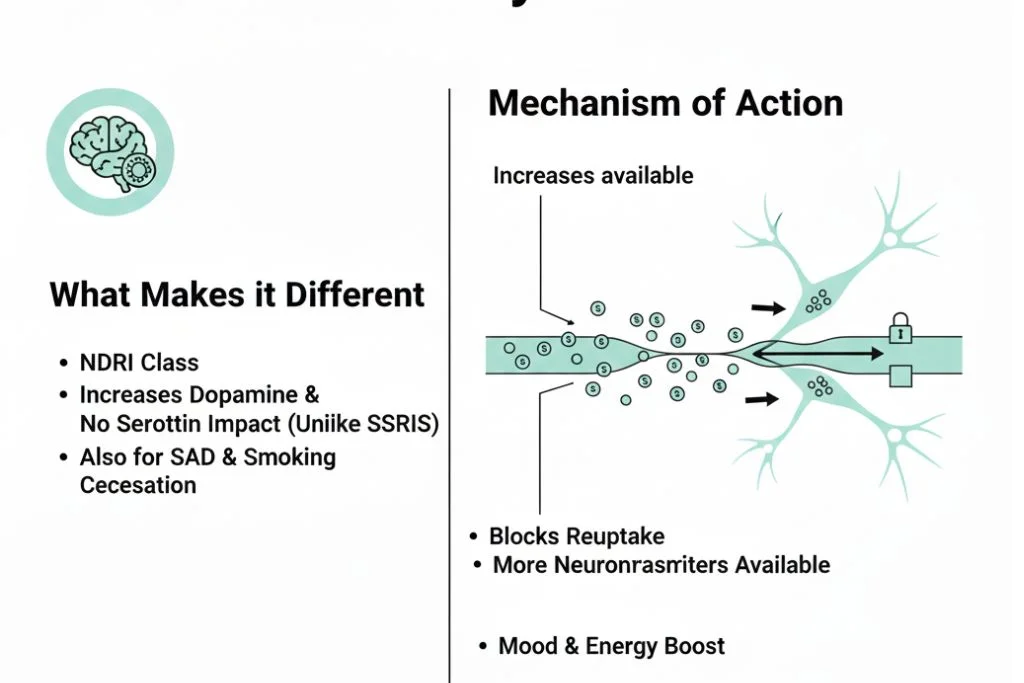
Wellbutrin is classified as a norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitor (NDRI).
Think of dopamine and norepinephrine as the brain’s natural energy and motivation chemicals. When you have depression, the levels of these chemicals can be low.
- Action: Wellbutrin works by blocking the reabsorption (reuptake) of these two chemicals back into the nerve cells.
- Result: This leaves more dopamine and norepinephrine available in the space between nerve cells, boosting mood, energy, and focus. This stimulant quality is why it often helps with fatigue and can be useful for those struggling to quit smoking.
Primary Uses: More Than Just Depression
While Wellbutrin is widely used to treat Major Depressive Disorder, its unique actions make it useful for other specific conditions:
- Major Depressive Disorder (MDD): It is effective for improving mood, energy, and concentration, particularly in patients who experience the lethargy and excessive sleeping associated with depression.
- Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD): The extended release version is specifically approved to prevent depressive episodes in people who suffer from SAD during the fall and winter months.
- Smoking Cessation (Zyban): The same active ingredient, bupropion, is sold under the brand name Zyban to help people quit smoking. It works by reducing cravings and withdrawal symptoms, likely because it affects the brain’s reward pathways mediated by dopamine.
- ADHD (Off-Label): Because it affects norepinephrine and dopamine, Wellbutrin is sometimes used to help manage the symptoms of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), particularly when traditional stimulants are not well tolerated.
Starting Wellbutrin: What to Expect
When you begin taking Wellbutrin, your doctor will start you on a low dose and increase it gradually. This slow approach helps your body adjust and minimizes side effects.
- Initial Boost (Days 1-7): You might feel a subtle increase in energy or a reduction in appetite quickly, due to the stimulant effect. You may also experience temporary mild headaches or dry mouth.
- Mood Improvement (Weeks 2-4): It takes time for the medication to build up effectively and change your mood. Don’t get discouraged if you don’t feel better right away.
- Full Effect (Weeks 6-8): The full, therapeutic benefit is usually noticeable around two months after starting the medication.
Most Important Risk: Seizure Threshold
This is the most critical safety point regarding Wellbutrin: it lowers the seizure threshold.
This means that if you have a history of seizure disorder (epilepsy), or if you have a condition that makes seizures more likely, Wellbutrin is generally not the right choice for you.
- Clinical Insight: The risk of seizure increases dramatically with dose. This is why doctors are very careful never to prescribe more than 450 mg per day. The risk is also higher if you have conditions like bulimia or anorexia nervosa, which cause electrolyte imbalances, or if you are withdrawing from alcohol or sedatives. Always tell your doctor about any history of seizures or eating disorders.
Common Side Effects: Dry Mouth and Insomnia
Because Wellbutrin acts as a stimulant, its most common side effects are often related to increased activation.
| Side Effect | Why It Happens | Practical Guidance |
| Insomnia | Increased norepinephrine causes wakefulness. | Take the medication in the morning or early afternoon; avoid taking it close to bedtime. |
| Dry Mouth | A common anticholinergic effect. | Drink plenty of water; chew sugar-free gum or suck on sugar-free hard candies. |
| Headaches | Often temporary as your body adjusts. | Manage with over-the-counter pain relievers if needed; headaches usually fade within a few weeks. |
| Anxiety/Agitation | Related to the dopamine and norepinephrine boost. | If severe, the dosage may need to be lowered or combined with a calming medication temporarily. |
Important Note on Weight: Unlike many SSRIs, Wellbutrin is often associated with weight loss or weight stability, not weight gain. This is a significant benefit for many patients, especially those who have struggled with weight on other antidepressants.
When to Contact Your Doctor Immediately
While most side effects are manageable, certain reactions require immediate medical attention:
- Signs of an Allergic Reaction: Hives, difficulty breathing, or swelling of the face, tongue, or throat.
- Severe Anxiety or Panic Attacks: If your anxiety becomes severe and unmanageable.
- Changes in Vision or Eye Pain: Especially in people with narrow angle glaucoma.
- Suicidal Thoughts or Worsening Depression: As with all antidepressants, monitor closely, particularly when starting or changing the dose.
Final Advice
Wellbutrin can be a highly effective medication for depression, seasonal struggles, and overcoming nicotine dependence. Its unique profile makes it a great choice for patients who need an energy boost or who wish to avoid the common weight and sexual side effects of other drug classes.
However, consistency is key. Take it exactly as prescribed, and do not stop taking it suddenly. If you decide you want to stop, always work with your physician to create a safe tapering schedule to avoid withdrawal effects. Your journey to better mental health is a partnership, and communication with your healthcare provider is your best tool.