In GHK-Cu peptide research, scientists focus on how this small copper complex behaves under analytical scrutiny. GHK-Cu is a copper-binding tripeptide, most often supplied as a lyophilized powder in 2 mg and 50 mg formats. These formats support both exploratory experiments and more demanding method development.
To use GHK-Cu effectively in a research setting, you need three things:
- A clear understanding of its chemical structure and copper coordination.
- Reliable methods to confirm identity and purity.
- A practical approach to stability and handling in the lab.
This guide organizes those elements into a structured workflow you can apply directly in analytical practice.
Understanding GHK-Cu as a Copper-Binding Tripeptide
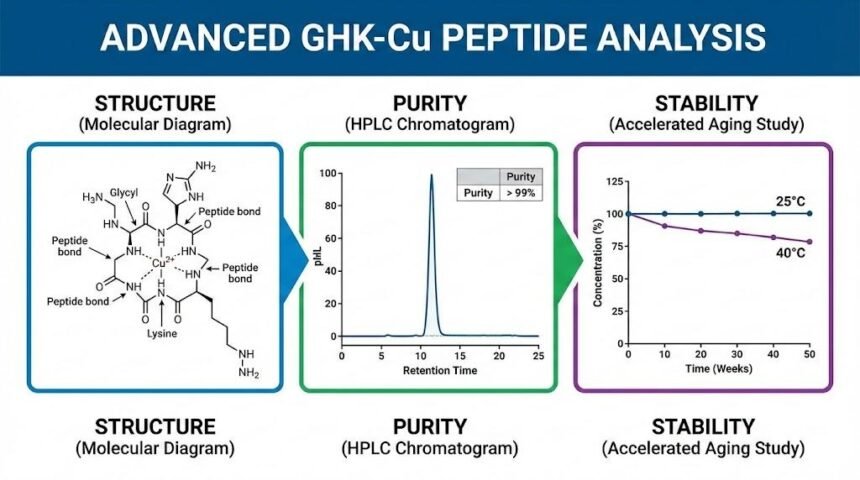
Core Structure of GHK-Cu
GHK-Cu forms when the tripeptide Gly–His–Lys (GHK) coordinates a copper(II) ion. The peptide sequence provides several critical binding sites.
- The N-terminal amino group can coordinate to copper.
- The histidine imidazole ring provides a strong metal-binding site.
- Backbone carbonyls and side-chain groups help stabilize the complex.
This coordination turns a simple tripeptide into a defined copper-binding tripeptide with distinct analytical behavior. Copper binding changes the electronic environment, thereby shifting UV–Vis absorbance, altering retention on reversed-phase HPLC, and modifying the mass spectral signature.
Researchers often treat GHK-CU Peptide as a compact model for metal–peptide interaction. Its small size and clear coordination pattern make it easier to interpret chromatograms and spectra than with more extended, more flexible sequences.
Role of 2MG and 50 MG Powder in Research Design
The molecule remains the same in both GHK-Cu 2MG and GHK-Cu 50 MG formats—only the available quantity changes, which affects how you design your work.
- 2MG vials are suitable for small feasibility studies and basic system checks.
- 50 MG vials support extended method development and repeated validation runs.
In GHK-Cu peptide research, many labs use the smaller format for initial screening, then switch to the larger fill size for long-term projects. This approach limits material waste while keeping method optimization flexible.
Analytical Framework for GHK-Cu Peptide Research
Using HPLC to Profile Purity and Related Species
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) sits at the core of GHK-Cu peptide research. Reversed-phase HPLC (RP-HPLC) is usually the first choice for purity assessment.
Key steps and considerations include the following points.
- Column selection
- Start with a C18 column suited to small peptides. Choose a particle size that balances backpressure and resolution.
- Mobile phase and gradient
- Use water and acetonitrile or methanol with a volatile acid modifier. Build a gradient strong enough to elute GHK-Cu cleanly but gently.
- Detection conditions
- Monitor at a UV wavelength where peptides absorb reliably. Track the central peak and any minor related components.
When the method performs well, you see a single dominant peak for the copper complex. Minor peaks represent free peptide, oxidized variants, or degraded fragments. Retention time stays stable across injections and lots.
This profile helps you judge batch quality and monitor stability over time.
Mass Spectrometry for Structural Confirmation
Mass spectrometry (MS) confirms the identity of GHK-Cu at the molecular level. In GHK-Cu peptide research, MS answers three key questions.
- Does the observed mass match the expected GHK-Cu complex?
- Is copper present in the correct oxidation state?
- Does the fragmentation pattern match the Gly–His–Lys sequence?
In practice, you inject the sample from HPLC or use direct infusion. You then observe the primary molecular ion peak that includes the copper ion. Next, you inspect the isotopic pattern driven by copper isotopes. Finally, you use MS/MS to generate fragments that map the peptide backbone.
These steps allow you to confirm the correct assembly of the complex and detect subtle changes, such as oxidation, deamidation, or partial copper loss.
Spectroscopic Tools to Study Copper–Peptide Interaction
Spectroscopic techniques provide additional insight that complements HPLC and MS.
- UV–Vis spectroscopy
- Track characteristic absorbance features from copper–ligand charge transfer. Monitor shifts in λmax under different pH or solvent conditions.
- FTIR spectroscopy
- Examine amide I and II bands from the peptide backbone. Observe changes in functional group environments after copper binding.
- Circular dichroism (CD), where available
- Evaluate conformational preferences of the peptide with and without copper.
When you combine these methods, you create a multidimensional fingerprint for GHK-Cu. That fingerprint anchors your GHK-Cu peptide research and guides quality decisions.
Stability Considerations for GHK-Cu 2MG and 50 MG Powder
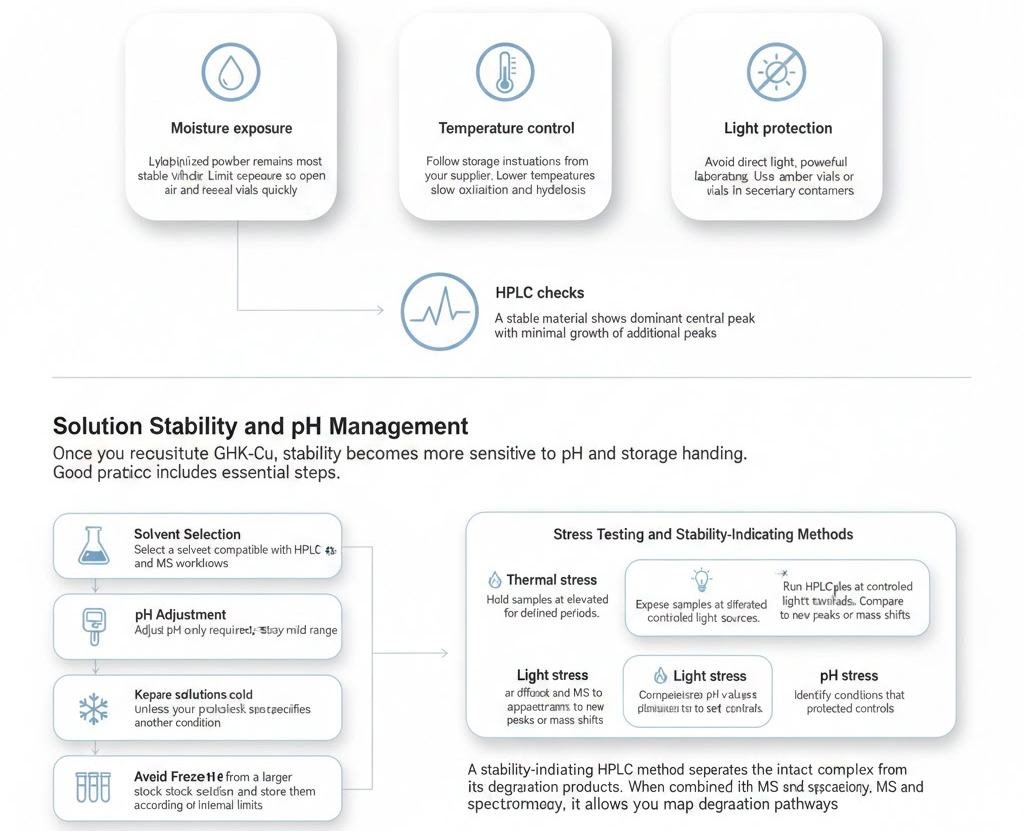
Solid-State Stability: Light, Heat, and Moisture
Stability directly affects data quality. You must keep the GHK-Cu 2MG and 50 MG powders in controlled conditions.
Focus on three primary factors.
- Moisture exposure
- Lyophilized powder remains most stable when dry. Limit exposure to open air and reseal vials quickly.
- Temperature control
- Follow storage instructions from your supplier. Lower temperatures usually slow oxidation and hydrolysis.
- Light protection
- Avoid direct light, powerful laboratory lighting. Use amber vials or store vials in secondary containers.
You can confirm solid-state stability by running periodic HPLC checks. A stable material shows a dominant central peak with minimal growth of additional peaks.
Solution Stability and pH Management
Once you reconstitute GHK-Cu, stability becomes more sensitive to pH and storage handling.
Good practice includes several essential steps.
- Select a solvent compatible with HPLC and MS workflows.
- Adjust pH only when required, and stay near a mild range.
- Keep solutions cold unless your protocol specifies another condition.
Avoid repeated freeze–thaw cycles. Instead, prepare aliquots from a larger stock solution and store them according to your internal limits. This strategy reduces stress on the copper-binding tripeptide and maintains consistent analytical results.
Stress Testing and Stability-Indicating Methods
To understand how GHK-Cu behaves over time, you can design stability studies.
- Thermal stress
- Hold samples at elevated temperatures for defined periods. Run HPLC and MS to track the appearance of new peaks or mass shifts.
- Light stress
- Expose samples to controlled light sources. Compare chromatograms to protected controls.
- pH stress
- Incubate solutions at different pH values for set durations. Identify conditions that produce rapid degradation.
A stability-indicating HPLC method separates the intact complex from its degradation products. When combined with MS and spectroscopy, it allows you to map degradation pathways and define safe handling windows for the material.
Positioning GHK-Cu Within Synthetic Research Peptides Workflows
Using GHK-Cu as a Method Development Model
Into a broader portfolio of synthetic research peptides, GHK-Cu serves as a practical benchmark. Its precise copper coordination and compact size make it ideal for several tasks.
- Testing new HPLC gradients and column chemistries.
- Evaluating instrument sensitivity and response consistency in MS.
- Comparing metal-bound peptides with metal-free analogs during method setup.
You can use the GHK-Cu 2MG format for early experiments. Once the method responds reliably, you move to 50 MG vials for extensive system suitability testing and cross-batch comparisons.
Practical Handling Steps for Reliable Results
To keep your GHK-Cu peptide research reliable, build simple handling routines.
- Before opening the vial
- Allow the vial to reach room temperature if stored cold. Check the label, lot number, and expiry date.
- During reconstitution
- Use clean, appropriate-grade solvents: record final concentration, solvent type, and pH.
- After reconstitution
- Filter solutions if your method requires particle-free samples. Create small aliquots to avoid frequent thawing. Label each aliquot with date and concentration.
- During analysis
- Run system suitability injections with GHK-Cu before unknown samples. Monitor retention time, peak area, and peak shape as quick quality indicators.
These steps help your lab generate data that remains consistent over time and across operators.
Documentation, Data Integrity, and Supporting Resources
Record-Keeping for Reproducible GHK-Cu Peptide Research
Robust records are essential in GHK-Cu peptide research. Good documentation ties each analytical result to the specific materials and conditions used.
At a minimum, record the following details.
- Product name, fill size, and supplier.
- Lot number and storage history for each vial.
- Reconstitution protocol, including solvent and pH used.
- HPLC, MS, and spectroscopic settings for each analytical run.
- Any deviations from your standard operating procedures.
You can then link unusual results to specific events, such as temperature excursions or extended storage in solution.
Using External Resources Alongside Internal Validation
External resources offer helpful context, but your in-house data remains the final reference. Use publications, reviews, and technical notes to compare your observed spectra and refine your understanding of copper coordination.
For a broader analytical context, you may consult specialist platforms, such as guides on advanced peptide analytics. Combine that information with your own validated protocols to build a reliable, lab-specific framework.
Conclusion
GHK-Cu provides a compact, well-defined model for GHK-Cu peptide research in analytical environments. As a copper-binding tripeptide, it offers clear structural features, strong metal coordination, and distinct analytical signatures, making it well-suited to HPLC, MS, and spectroscopy.
When you control storage conditions, design stability-indicating methods, and maintain strong documentation, GHK-Cu becomes a dependable tool. It supports method development, system suitability testing, and broader metal–peptide studies within a strict research-only framework.
By applying the practical steps outlined here, you can improve data quality, enhance reproducibility, and extract more value from every GHK-Cu peptide research project you run in the laboratory.
Disclaimer
This information is provided for research, educational, and informational purposes only. GHK-Cu discussed here refers to research-grade material not intended for medical, cosmetic, therapeutic, or human use. Always follow your institution’s safety rules, use proper laboratory practices, and rely on qualified professionals for any experimental decisions.