It can be concerning to notice a lump or swelling along your jawline. This area houses many important structures, including lymph nodes, salivary glands, muscles, and bone, all of which can become inflamed or enlarged. While many causes are minor, like a common cold or a dental issue, persistent or painful swelling warrants attention. This article will guide you through the likely causes, offer practical self-care steps, and explain when it’s time to consult a healthcare professional.
Understanding the Jaw and Neck Region
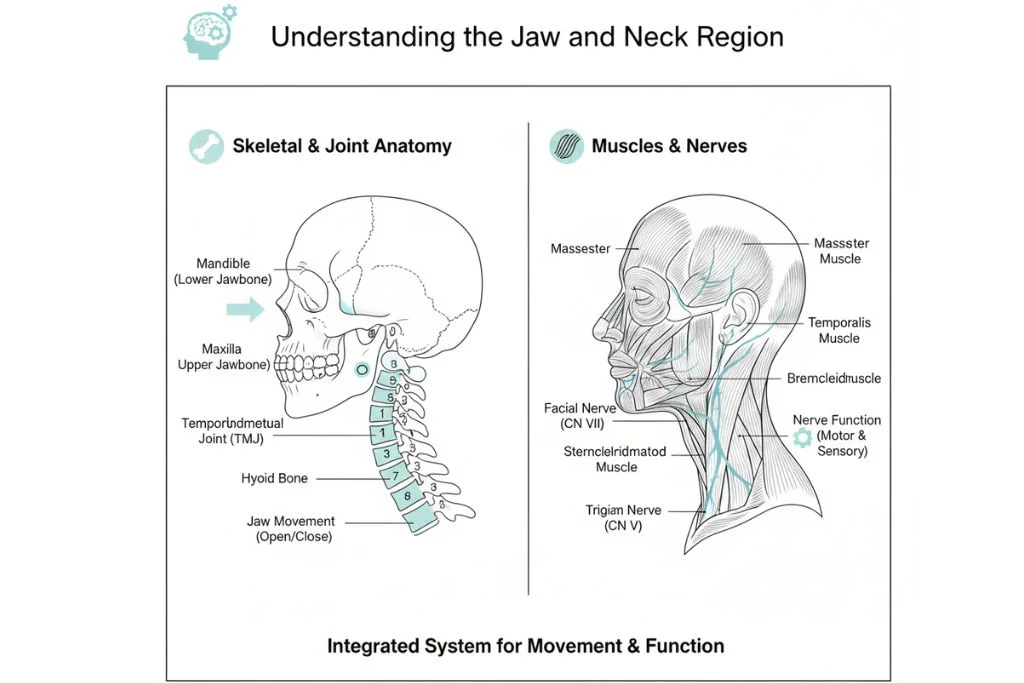
The jaw (mandible) and the surrounding soft tissues are complex. Swelling here is often a sign that your body is fighting an infection or reacting to an injury. The most common structures involved are:
- Lymph Nodes: These small, bean-shaped glands filter fluid and trap pathogens. They commonly swell in response to infections in the head, neck, or throat (e.g., strep throat, common cold).
- Salivary Glands: The parotid, submandibular, and sublingual glands can become swollen due to infection (mumps), a blockage (salivary stone), or inflammation.
- Teeth and Gums: Dental abscesses, wisdom tooth eruption, or severe gum infection can cause localized, often very painful, swelling in the jaw area.
- Muscles and Bone: Injuries (like a blow to the jaw) or conditions like temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders can lead to swelling and tenderness.
Common Causes of Jaw Swelling
Determining the cause is key to effective management. Below is a breakdown of the most frequent culprits:
Infectious Causes
| Condition | Typical Presentation | Self-Care / Initial Steps |
| Swollen Lymph Nodes | Usually bilateral (on both sides), soft, movable, often accompanied by fever or sore throat. | Rest, hydration, over-the-counter (OTC) pain relief (Ibuprofen, Acetaminophen). |
| Dental Abscess | Severe, throbbing, localized pain; tender to touch; may be accompanied by fever or bad taste in the mouth. | OTC pain relief, cool compress. Urgent dental review needed. |
| Mumps or Viral Sialadenitis | Swelling in front of the ear or under the chin (parotid or submandibular glands), often bilateral, with fever and malaise. | Rest, soft diet, hydration, warm compress. |
Non-Infectious Causes
- Salivary Gland Stone (Sialolithiasis): Intermittent swelling, often occurring or worsening when eating, which may suddenly resolve when the stone passes.
- Trauma/Injury: Swelling, bruising, and pain following an impact to the jaw or face.
- Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Disorder: Pain and swelling around the jaw joint (just in front of the ear), often accompanied by clicking, popping, or difficulty opening the mouth fully.
- Allergic Reaction (Angioedema): Rapid, significant swelling of the lips, tongue, or jawline, often with hives or difficulty breathing (this is a medical emergency).
Practical Guidance: Reducing Swelling and Pain
For non-urgent, infection-related, or minor injury, related swelling, the following simple steps can provide relief:
Step 1: Apply Temperature Therapy
Use a combination of both to manage inflammation and pain effectively.
- Cold Compress: Apply a cloth-wrapped ice pack to the swollen area for 15–20 minutes, three to four times a day for the first 24–48 hours. This helps constrict blood vessels and reduce initial swelling.
- Warm Compress/Heat: After the initial 48 hours (or for salivary gland issues), switch to a warm, moist cloth. Apply for 10–15 minutes several times a day. This can help increase circulation and promote drainage, especially for lymph nodes or gland issues.
Step 2: Dietary Modifications (Soft Foods)
Temporarily switching to a soft diet can reduce strain on the jaw muscles and joint, which can be aggravated by chewing.
| Foods to Include | Foods to Temporarily Avoid |
| Smoothies, Yogurt, Pudding | Hard candies, Nuts, Seeds |
| Scrambled eggs, Oatmeal | Chewy meats (steak, jerky) |
| Pureed soups, Mashed potatoes | Raw vegetables (carrots, celery) |
| Cooked/Flaked fish | Gum, Excessive yawning |
Step 3: Jaw Relaxation and Hygiene
- Rest the Jaw: Avoid clenching your teeth. Try to keep your teeth slightly apart, with your lips gently touching.
- Gentle Massage: If the swelling is due to a stiff muscle or TMJ, a very gentle massage in circular motions on the cheek/joint area can help release tension.
- Oral Rinse: For swelling related to a dental issue or sore throat, rinse with a warm saltwater solution (1 teaspoon of salt in 1 cup of warm water) 3-4 times a day.
Note: Never try to pop or drain a localized swelling (like an abscess) yourself. This can spread the infection.
Understanding Swelling Progression
Swelling is often the most noticeable in the first 24–48 hours. It should generally begin to slowly subside after this period as the underlying infection or inflammation resolves.
Swelling Improvement Timeline (General Guide)
| Underlying Cause | Expected Improvement Onset | Typical Resolution Time |
| Viral Infection (Lymph Nodes) | Day 3–5 | 1–3 weeks |
| Minor Injury/Strain (Muscle) | Day 2–3 | 5–7 days |
| Post-Dental Procedure | Day 1–2 | 3–5 days |
When to See a Doctor (Red Flags)
While minor causes often resolve with self-care, certain symptoms indicate a need for prompt medical or dental attention:
- Rapidly Worsening Swelling: Swelling that is increasing quickly over hours.
- Difficulty Breathing or Swallowing: This could indicate a severe infection (e.g., Ludwigs Angina) or a serious allergic reaction and requires emergency care (call your local emergency number).
- High Fever and Chills: Signs of a systemic or severe infection.
- Inability to Open Your Mouth Fully (Trismus): Suggests severe inflammation or a deep space infection.
- Swelling that is Rock-Hard and Fixed: Swelling that is not soft, movable, or tender, especially if it persists, may need investigation to rule out rarer, serious conditions.
- Swelling Persists: If the swelling does not begin to subside after 7 days, or if it is recurrent.
Final Advice
The jaw and neck area is sensitive. If the swelling is directly related to a tooth (severe pain, loose tooth), prioritize seeing a dentist immediately, as the infection must be treated at its source. For other causes, like widespread lymph node swelling with a cold, the best approach is supportive care and observation. Trust your instincts; if you are worried or the swelling is interfering with daily life, seek professional reassurance.
Medical Disclaimer
This article is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Mumps (Parotitis).
- American Academy of Otolaryngology—Head and Neck Surgery. Salivary Glands.
- American Dental Association (ADA). Abscesses.

