If you have ever noticed that the skin around your genitals looks darker than the rest of your body, you are not alone. This is one of the most common questions dermatologists and gynecologists hear. Still, because of that, it is rarely talked about openly. Many people worry in silence or turn to unsafe advice online.
Let’s be clear from the start.
Genital hyperpigmentation is commonly standard and usually harmless.
What Hyperpigmentation Really Means
Hyperpigmentation means that some regions of skin produce more melanin than others. Melanin is the natural pigment that gives skin its color.
The genital area naturally has
- thinner skin
- more friction
- stronger hormonal influence
Because of this, it often appears darker than the arms’ faces or stomachs. This does not mean something is wrong.
A dermatologist once explained it like this.
“The genital area is designed for flexibility and protection not uniform color. Pigment is part of that protection.”
That explanation alone reassures many patients.
Why the Genital Area Is Prone to Darkening
Unlike sun spots or age spots, genital hyperpigmentation is rarely caused by sunlight. Instead, it develops slowly due to internal and mechanical factors.
Hormones Are the Biggest Factor
Hormones strongly influence melanin production.
Darkening often becomes noticeable during
- puberty
- pregnancy
- use of hormonal birth control
- perimenopause and menopause
Estrogen and progesterone stimulate pigment cells. That is why some people notice darkening even without weight change or irritation.
A real example
One woman noticed darker labial skin during pregnancy and assumed it was permanent damage. Six months after delivery, the color softened naturally without any treatment.
Friction and Daily Movement Matter More Than You Think
Friction is one of the most underestimated causes.
Common sources include
- tight underwear
- tight jeans or leggings
- inner thighs rubbing
- frequent walking or exercise
- shaving and waxing
When skin is repeatedly irritated, the body responds by producing more melanin. This is called post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
This is not a failure of hygiene. It is a typical skin defense response.
Genetics plays a Quiet but Powerful Role.
Some people are more prone to pigmentation.
If you have
- darker skin tone
- family history of pigmentation
- pigmentation in the underarms or inner thighs
Then, genital hyperpigmentation is expected. It does not mean you did anything wrong.
Aging Changes Skin Behavior
As skin ages
- collagen decreases
- skin becomes thinner
- pigment distribution becomes uneven
This can make the contrast more noticeable, even if the pigment itself has not increased dramatically.
Areas Commonly Affected
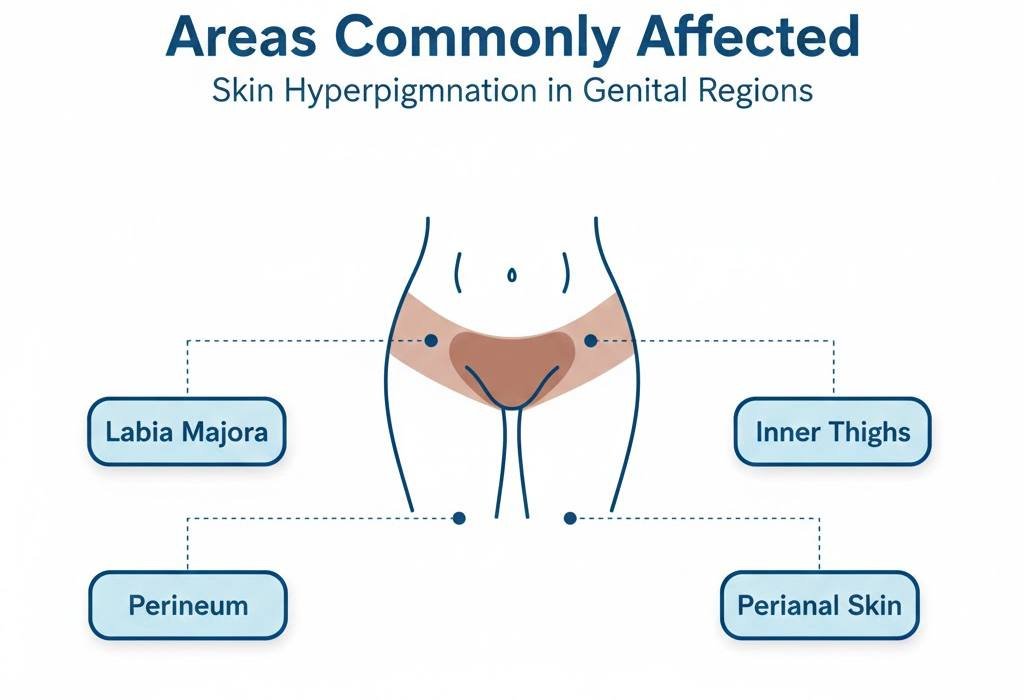
Genital hyperpigmentation rarely involves only a single small spot. It usually appears in areas under pressure or in motion.
Most common areas
- labia majora
- inner thighs
- perineum
- skin around the anus
This pattern helps doctors distinguish normal pigmentation from medical conditions.
What Is Normal and What Is Not
Normal
- gradual darkening over the years
- A darker color without pain or itching
- symmetrical color on both sides
Needs medical review
- sudden rapid darkening
- thick velvety texture
- itching, burning, or pain
- irregular patches with rash
One condition doctors watch for is acanthosis nigricans, which may signal insulin resistance. This is uncommon, but it is essential to rule out if texture changes occur.
Biggest Mistakes People Make
Many people worsen pigmentation by trying to fix it aggressively.
Common mistakes
- scrubbing with loofahs or brushes
- using lemon, baking soda, or toothpaste
- applying strong acids meant for the face
- using bleaching creams without supervision
A dermatologist once said
“Most genital pigmentation problems I treat are caused by treatments people tried to fix pigmentation.”
Gentle care prevents more darkening better than any product.
Daily Habits That Actually Help
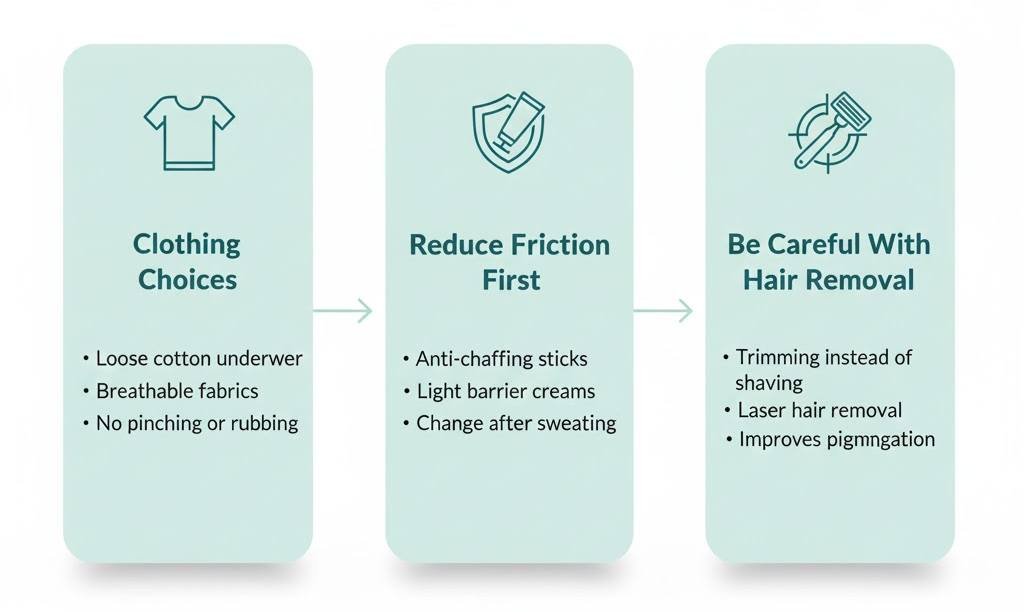
These changes sound simple, but they make the most significant difference in the long term.
Clothing Choices
Choose
- loose cotton underwear
- breathable fabrics
- clothing that does not pinch or rub
Avoid wearing tight leggings all day, especially in the heat.
Reduce Friction First Before Using Products
If friction continues, no cream will work.
Helpful options
- silicone-based anti-chafing sticks
- light barrier creams on inner thighs
- changing clothes after sweating
Even professional treatments fail if friction is not addressed.
Be Careful With Hair Removal
Shaving and waxing create microinflammation.
If pigmentation worsens after hair removal, consider
- trimming instead of shaving
- Laser hair removal with a qualified provider
Laser hair removal often improves pigmentation indirectly by reducing irritation.
Gentle Skincare That Is Actually Safe
Genital skin is not facial skin. Less is more.
Ingredients Dermatologists Trust
- Niacinamide reduces pigment transfer and calms skin
- Azelaic acid gently reduces pigment production
- Low-strength kojic acid in professional formulations
- Vitamin C in stable, low-irritation formulas
These work slowly but safely.
Ingredients to Avoid Unless Prescribed
- hydroquinone
- strong glycolic acid
- Retinoids are not designed for sensitive skin
- fragrance and alcohol
Stronger is not better in this area.
A Simple Daily Routine That Works
Morning
- Rinse with water only
- Pat dry gently
- Apply a light barrier or moisturizer if friction occurs
Evening
- gentle cleanse if needed
- pat dry
- Apply the recommended topical treatment
Consistency matters more than strength.
Professional Treatments When Needed
Some people want medical help, and that is okay.
Dermatologists may offer
- prescription pigment creams
- mild chemical peels designed for intimate skin
- laser treatments with conservative settings
These treatments require expertise. Never attempt home versions.
Real-life example
A patient with long-term inner thigh pigmentation improved by 40% after three gentle peel sessions combined with friction reduction. The doctor emphasized that lifestyle change was as significant as the peel.
How Long Does Improvement Take
This is slow skin.
Typical timeline
- Reduced irritation shows improvement in one month
- creams show a change in two to three months
- procedures take three to six months
Anyone promising instant results is not being honest.
Mental and Emotional Side of This Issue
Many people feel embarrassed about genital pigmentation because of unrealistic images online.
Doctors see this daily.
Normal bodies vary in color, texture, and shape.
One gynecologist said
“The expectation of uniform genital skin is not biological it is cultural.”
That perspective helps many patients feel less alone.
When to Talk to a Doctor
You should see a professional if
- color changes suddenly
- texture becomes thick or itchy
- pain or rash appears
- pigmentation spreads rapidly
A short visit can provide peace of mind.
Final Thoughts
Genital hyperpigmentation is one of the most misunderstood body changes. Hormones, friction, and genetics usually influence it.
Healthy skin is the goal, not perfect color.
Gentle care, patience, and realistic expectations protect both your skin and your confidence.
If you ever feel unsure, talk to a dermatologist or gynecologist. You deserve clear answers without judgment.