Digestive discomfort is something many people experience from time to time, whether it’s the discomfort of constipation or the burning feeling of indigestion and heartburn. For many years, Milk of Magnesia (MoM) has been a trusted over-the-counter option for easing these common digestive problems. Known for its gentle yet effective action, it helps support digestive relief when used correctly and with proper care.
What Is Milk of Magnesia and How Does It Work?
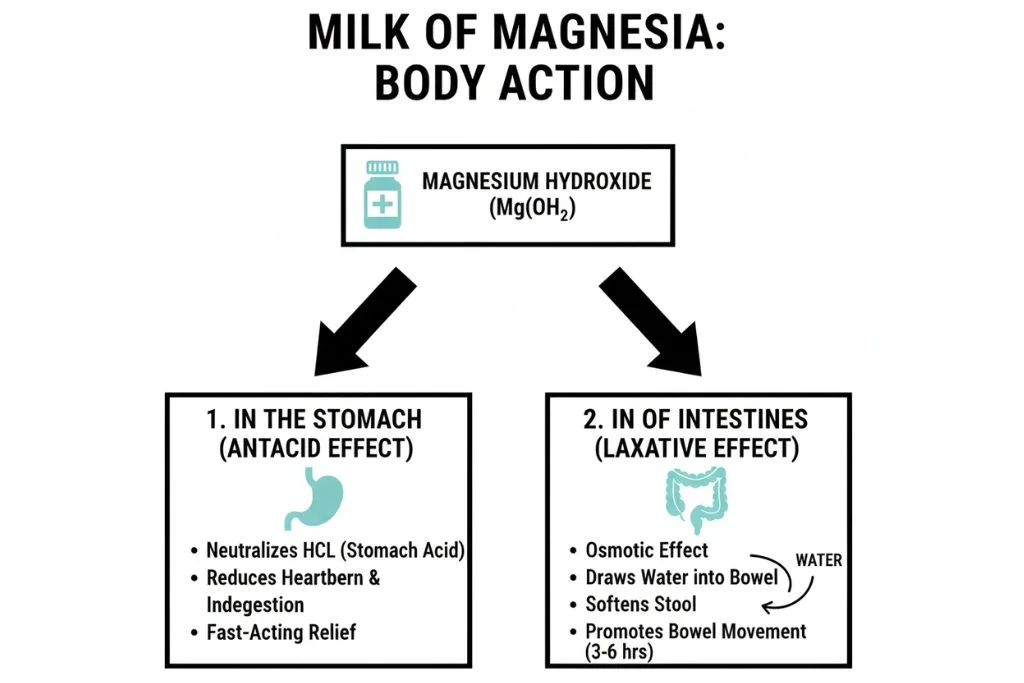
Milk of Magnesia (MoM) is a liquid suspension of magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)₂). It works in two main ways, depending on the dose and what you need it for:
1. Laxative (Relieves Constipation)
- How it works: Magnesium hydroxide is not fully absorbed by the body. It draws water into the intestines, softening the stool and increasing its bulk. This helps the intestines contract, moving stool along.
- Use: Helps relieve occasional constipation, usually within 30 minutes to 6 hours.
2. Antacid (Relieves Indigestion or Heartburn)
- How it works: Magnesium hydroxide neutralizes excess stomach acid. Chemically, it reacts with hydrochloric acid (HCl) in the stomach:
Mg(OH)2+2HCl→MgCl2+2H2O
This reaction reduces stomach acidity and eases symptoms.
- Use: Provides fast relief from heartburn, sour stomach, or indigestion.
Dosage and Administration: A Step-by-Step Guide
Dosage and Timing
The correct dose of Milk of Magnesia (MoM) depends on whether you are treating constipation or heartburn. Always use the measuring device that comes with the product and follow the instructions on the label or your healthcare provider’s guidance.
How to Take It
- Route: Oral (drink the liquid)
- Tip: Shake the bottle well before each use to mix the magnesium evenly
Key Safety Tips
- Drink Water: When using MoM as a laxative, always take it with a full glass (8 oz) of water to help it work properly.
- Limit Use: Do not take the maximum dose for more than 7 days unless your doctor says it’s okay.
- Medication Interactions: Magnesium can reduce the effectiveness of some antibiotics and heart medications. Take MoM at least 2–4 hours apart from these drugs.
Example Step-by-Step (Constipation, Adult Dose)
- Shake the bottle well.
- Measure the recommended dose (usually 30–60 mL).
- Take the dose and immediately drink a full glass of water.
- Repeat no more than once every 24 hours, or as directed by your doctor.
Side Effects and Management
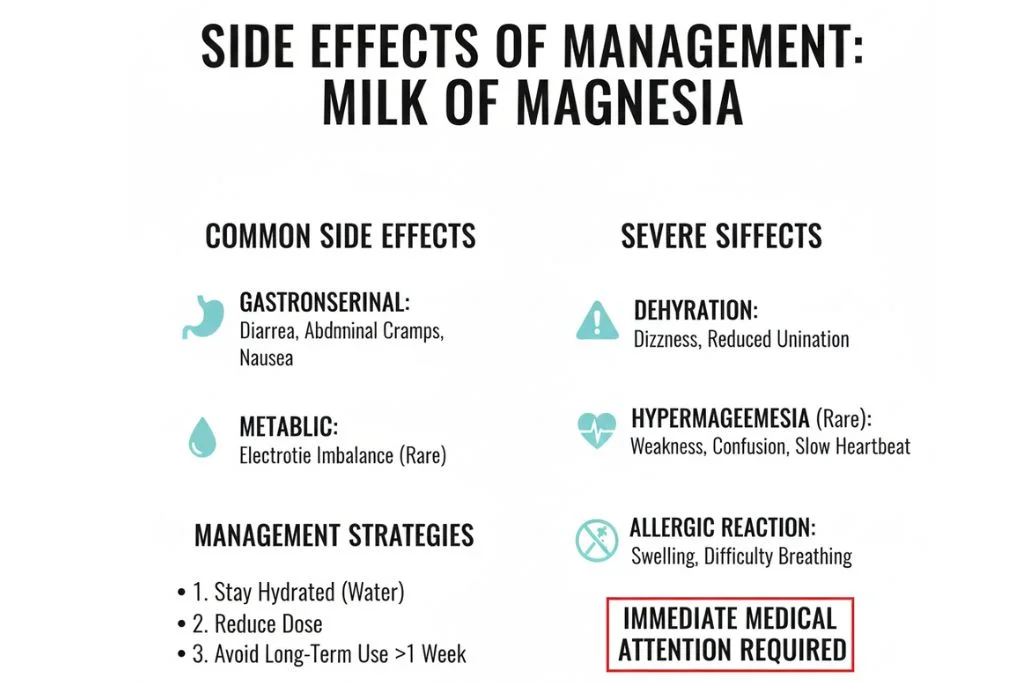
Milk of Magnesia is usually well-tolerated when taken for a short period and at the correct dose. However, some side effects can occur because of its magnesium content.
Common Side Effects (Usually Mild and Dose-Related)
- Gastrointestinal: Diarrhea, abdominal cramps, nausea.
- Metabolic: Electrolyte imbalance (rare with short-term use).
Graph: Dose-Related Side Effects (ASCII Table)
| Dosage Goal | Primary Therapeutic Effect | Most Common Side Effect |
| Low Dose (5-15 mL) | Antacid/Acid Neutralization | Minimal Diarrhea Risk |
| Standard Dose (30-60 mL) | Laxative/Bowel Movement | High Risk of Diarrhea/Cramps |
Serious Side Effects (Require Immediate Medical Attention)
These side effects are uncommon, especially in people with healthy kidneys, but they can be serious:
- Severe diarrhea or dehydration: Persistent watery stools that may cause dizziness or reduced urination.
- Hypermagnesemia (too much magnesium): Mainly affects people with kidney problems. Signs include muscle weakness, confusion, slow heartbeat, or difficulty breathing.
- Allergic reactions: Swelling of the face, tongue, or throat, or trouble breathing.
Note: If any of these occur, seek medical attention immediately.
Special Populations and Contraindications
Although Milk of Magnesia (MoM) is generally safe, certain groups should use it with caution.
Key Precautions
- Kidney Disease: Magnesium is removed from the body by the kidneys. People with impaired kidney function risk magnesium buildup (hypermagnesemia). Consult a doctor before use.
- Abdominal Pain: Do not take MoM if you have sudden abdominal pain, vomiting, or signs of appendicitis or bowel blockage.
- Fluid Restriction: Use carefully if you are on strict fluid limits for medical reasons.
Risk Assessment: Who Should Be Careful
| Population | Condition / Risk | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| Elderly | Possible kidney decline | Use lower dose; monitor for weakness |
| Pregnant / Breastfeeding | Generally safe for laxative use | Consult a doctor for proper dosage |
| Chronic Kidney Failure | High risk of hypermagnesemia | Avoid or use only under medical supervision |
Practical Lifestyle and Dietary Tips
To enhance the effects of MoM for constipation and support long-term digestive health, incorporate these tips.
Dietary Guidance (Supporting Bowel Function)
| Eat More (Fiber & Fluid) | Limit (Constipating/Irritating Foods) |
| High-fiber fruits (prunes, berries) | Highly processed foods |
| Whole grains (oats, brown rice) | Red meat and dairy (in excess) |
| Plenty of water and clear liquids | Excessive caffeine and alcohol |
Comfort Measures (Post-Dosing)
- Fluid Intake: Drink water consistently throughout the day to aid the osmotic action.
- Activity: Gentle activity, like walking, helps stimulate bowel movement and reduces cramping.
- Timing: If using as a laxative, plan to be near a restroom, as the effects can be rapid.
Improvement Timeline
| Use | When Effects Start | Expected Duration / Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Antacid (Heartburn) | 5–15 minutes | Works with a single dose, as needed |
| Laxative (Constipation) | 30 minutes to 6 hours | Do not use for more than 7 consecutive days |
| Side Effects (Diarrhea) | Within 1–3 hours of taking | Usually stops shortly after stopping use |
Final Advice
Milk of Magnesia is an effective and fast-acting option for occasional constipation and heartburn. Use it carefully: stay well-hydrated and follow the recommended dosage and duration. If you need to use it frequently, this may indicate an underlying health issue that should be evaluated by a healthcare professional. Treating the root cause, not just the symptom, is key to your long-term well-being.
Medical Disclaimer
This article provides general information and should not be considered a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or before starting any new treatment.
References
- U.S. National Library of Medicine. (2024). Magnesium hydroxide. MedlinePlus. https://medlineplus.gov
- American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. (2023). Magnesium hydroxide. Drug Information. https://www.ashp.org
- Di Palma, J. A. (2018). Laxatives and cathartics. Clinics in Colon and Rectal Surgery, 31(1), 18–25. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0038-1636530
- Drug label information for Milk of Magnesia. (n.d.). Manufacturer-specific reference omitted for neutrality.

